Digital Image Correlation
Material Testing with Full-Field Strain Distribution Visualization
Materials, components or products are subjected to a wide variety of loads during their service life. Detailed and accurate measurements of the deformation, strain values and points of failure are essential to get insight in the overall mechanical behaviour. The most commonly used methods for measuring strain include strain gauges and extensometers, however they provide only one data point over an averaged area of application.
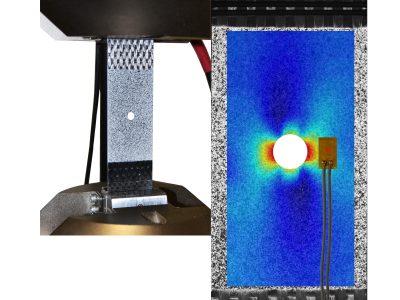
Digital Image Correlation (DIC) is a powerful measurement technique for providing a complete strain distribution data during mechanical characterization tests. Cameras are focused on the surface of an object or material and by tracking the motion of a specific speckle pattern applied on the material, all displacement and strain components can be extracted.
The biggest advantage of the technique is that it is completely contactless and independent on the size or material of the object under study and provides a full-field data distribution rather that one discrete data point. It can achieve high accuracy due to extensive calibration procedures allowing for displacement and strain resolutions of 1 µm and 50 µstrain, respectively.
For some materials it can be very challenging to adhere a strain gauge to the surface or attach an extensometer. For example soft materials such as textile fabrics, paper, foams or very thin films could be influence by the attachment of the sensors. The contactless digital image correlation system offers a stable and robust solution to al these challenges. When utilizing high speed cameras the technique can be readily applied during impact or high strain rate tests.
 Application fields:
Application fields:
- Static, dynamic and fatigue tests (standard or custom)
- High strain rate tension and compression
- Adhesive and cohesive properties
- Composite delamination
- Material or component failure and crack initiation points
The extracted data fields can be used to compare with finite element (FE) simulation and calibrate and validate material parameters and models.
 Digital Image Correlation features:
Digital Image Correlation features:
- Contactless and full-field distribution maps
- Independent of material type, geometry and size
- Accurate displacement and strain datasets
Application Example: Small Diameter Wire Compression Test
Quasi-static compression tests combined with in-situ full-field strain measurement using the Digital Image Correlation method.
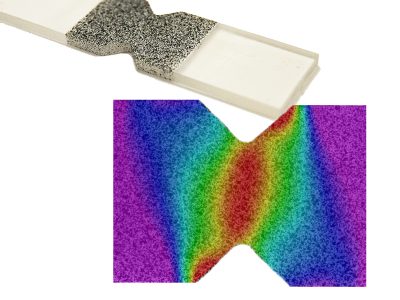
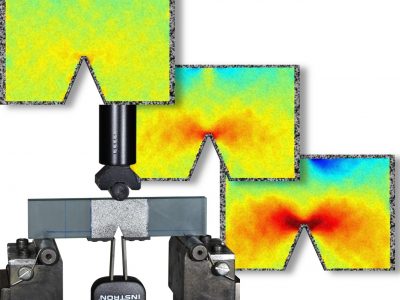
Application Example: V-notch Shear Test
Digital Image Correlation strain measurement makes it possible to measure full-field strains at a specific field-of-view area.